Data on SDCC
(formerly RACF (even earlier RCF))
Jakub Češka
Quick Glossary
- Run - a period of several months in a year when the accelerator conducts collisions
- e.g., Run17 - acceleration that took place (started) in 2017
- run - approximately 30-minute interval when data is collected; separated
- e.g., 17319001 (first run of Run17)
- collision type - collision system and center-of-mass energy
- e.g., pp 510GeV, AuAu 54GeV
- picoDst, MuDst - format of stored data
- most newer data primarily uses picoDst (newer format)
- production - specific data production, there can be several
- e.g., P20ic
- library - version of STAR software with which the data was produced
- e.g., SL22b
- data stream - type of data that the dataset contains
- e.g., st_physics
- Trigger - triggering mechanism that identifies “interesting” collisions
- e.g., BHT1*VPD30, BHT2*BBCMB
- storage - where a specific file is stored; we know 3 types:
- local - distributed disks (on a specific server), we use xrootd for access
- NFS (network file storage) - shared disks, we can access directly
- HPSS (high performance storage system) - tape storage, relevant for “more exotic” or older data
“Analyze 500 GeV proton-proton data from Run17 using BHT1 trigger. Find their luminosity for me.”
Act 1
How to Access the Data
Directory for data-related things
Directory containing links to pages where information about individual data can be found
Data for Physical Analysis - Overview

Production Datasets for Physics Analysis
List and brief description of datasets. Contains information about detectors used for data collection, trigger setups, list of individual data streams, link to the trigger page, list of individual production streams
Data for Physical Analysis - Example

Production Datasets for Physics Analysis
List and brief description of datasets. Contains information about detectors used for data collection, trigger setups, list of individual data streams, link to the trigger page, list of individual production streams
Act 2
How to Work with Triggers
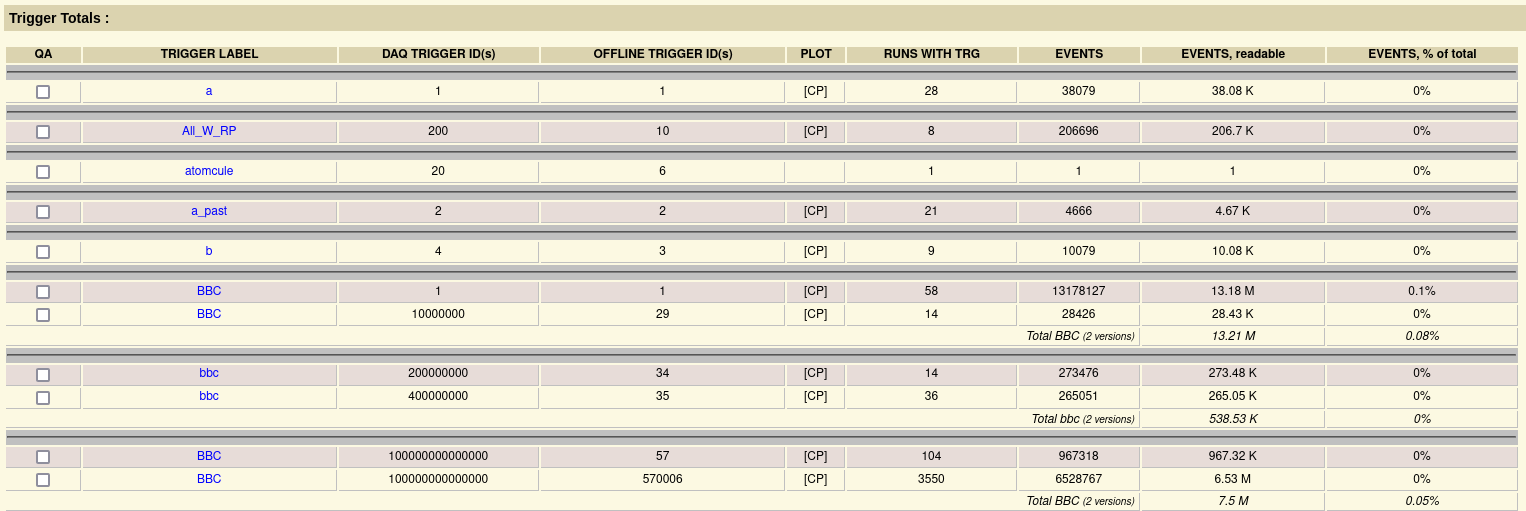
List of Triggers - Overview
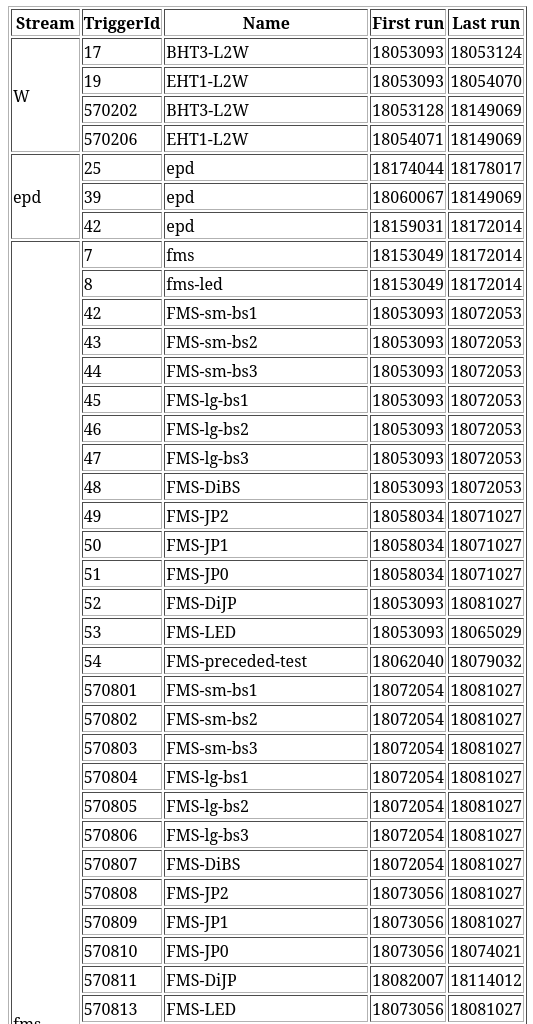
List of individual triggers, their IDs (those used in analysis) and which data stream they are in, the first and last run during which the given trigger was used
“Production triggers” are typically designated by a 6-digit number (if there is only 1 or 2 digits, it’s a test trigger from the beginning of the Run - not used)
Triggers sometimes have multiple components - component1*component2
E.g., BHT1 (energetic hit in the calorimeter) * VPD30 (vertex placed within 30 centimeters from the detector center in the beam direction)
List of Triggers - Physics
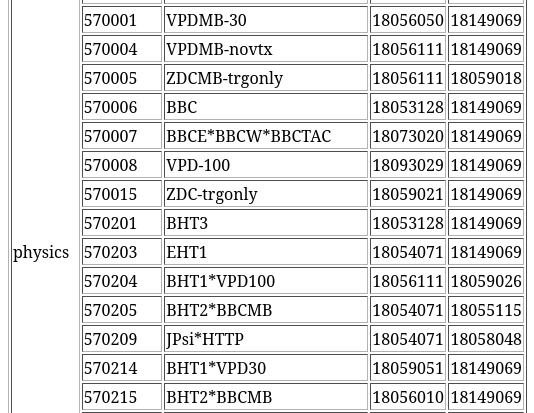
List of individual triggers, their IDs (those used in analysis) and which data stream they are in, the first and last run during which the given trigger was used
“Production triggers” are typically designated by a 6-digit number (if there is only 1 or 2 digits, it’s a test trigger from the beginning of the Run - not used)
Triggers sometimes have multiple components - component1*component2
E.g., BHT1 (energetic hit in the calorimeter) * VPD30 (vertex placed within 30 centimeters from the detector center in the beam direction)
INTERLUDE
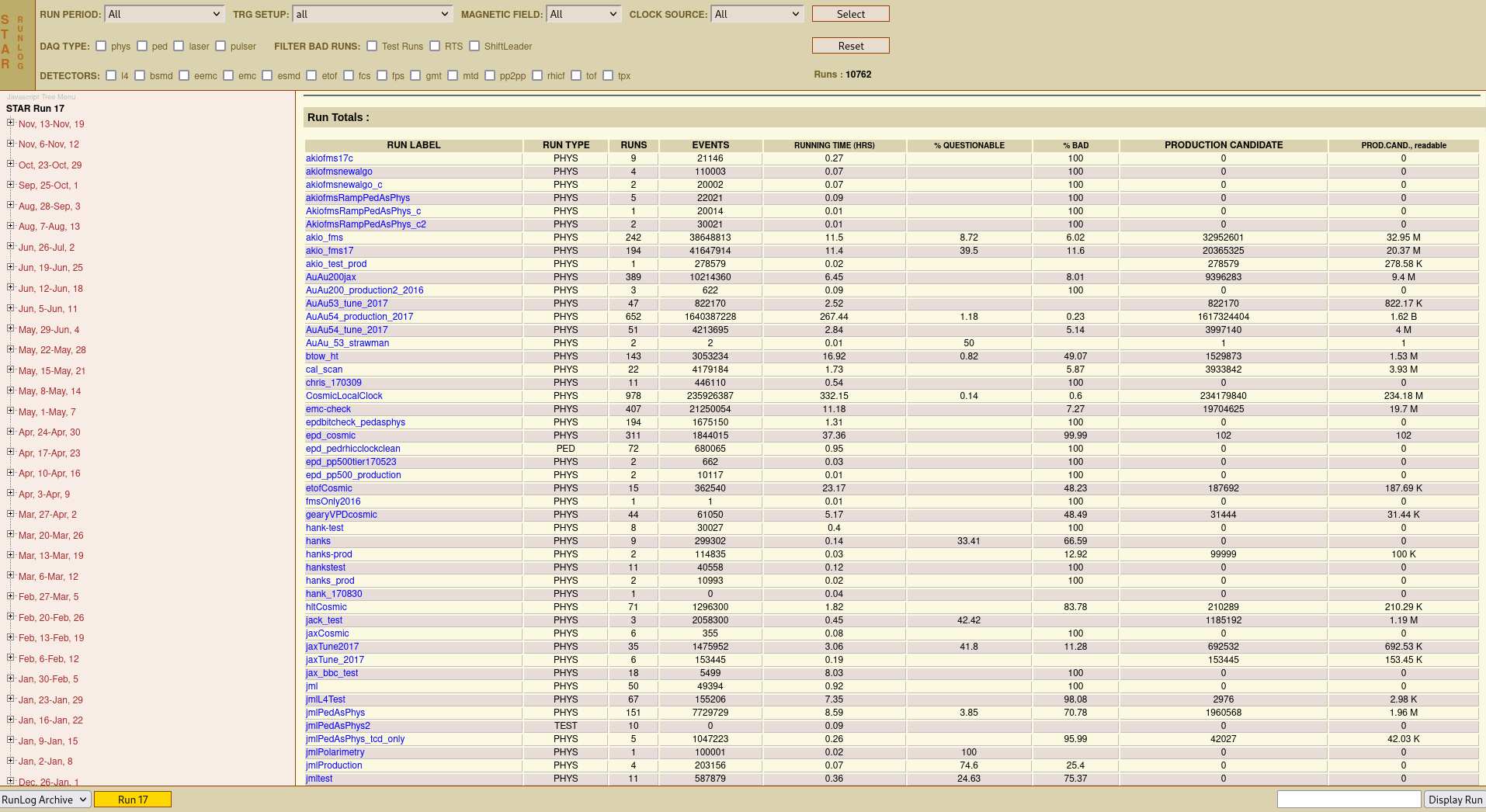
RunLog Browser
STAR Online
RunLog Browser - Introduction
RunLog Browser - Triggers
Act 3
Luminosity - What? Why? How?
Luminosity - Introduction
- Luminosity - “the ratio of the number of detected collisions $dN$ over time $dt$ and the cross-section ($\sigma$)”
L = \frac{1}{\sigma} \frac{\mathrm{d}N}{\mathrm{d}t}
Used to characterize the performance of the accelerator (number of collisions per unit time)
Typically has dimensions [b⁻¹ s⁻¹]
Integrated luminosity is important
L_\mathrm{int} = \int L \mathrm{d}t
Luminosity - Advanced
L = \frac{kN^2f}{4\pi \sigma_x^2 \sigma_y^2}
- k - number of bunches in the accelerator
- N - number of particles in a bunch
- f - revolution frequency
- σ - beam size at the collision point
How to Access Luminosity 1/4

↓

How to Access Luminosity 2/4
How to Access Luminosity 3/4

How to Access Luminosity 4/4

We Have Luminosity
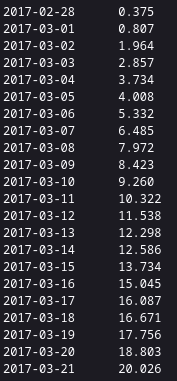
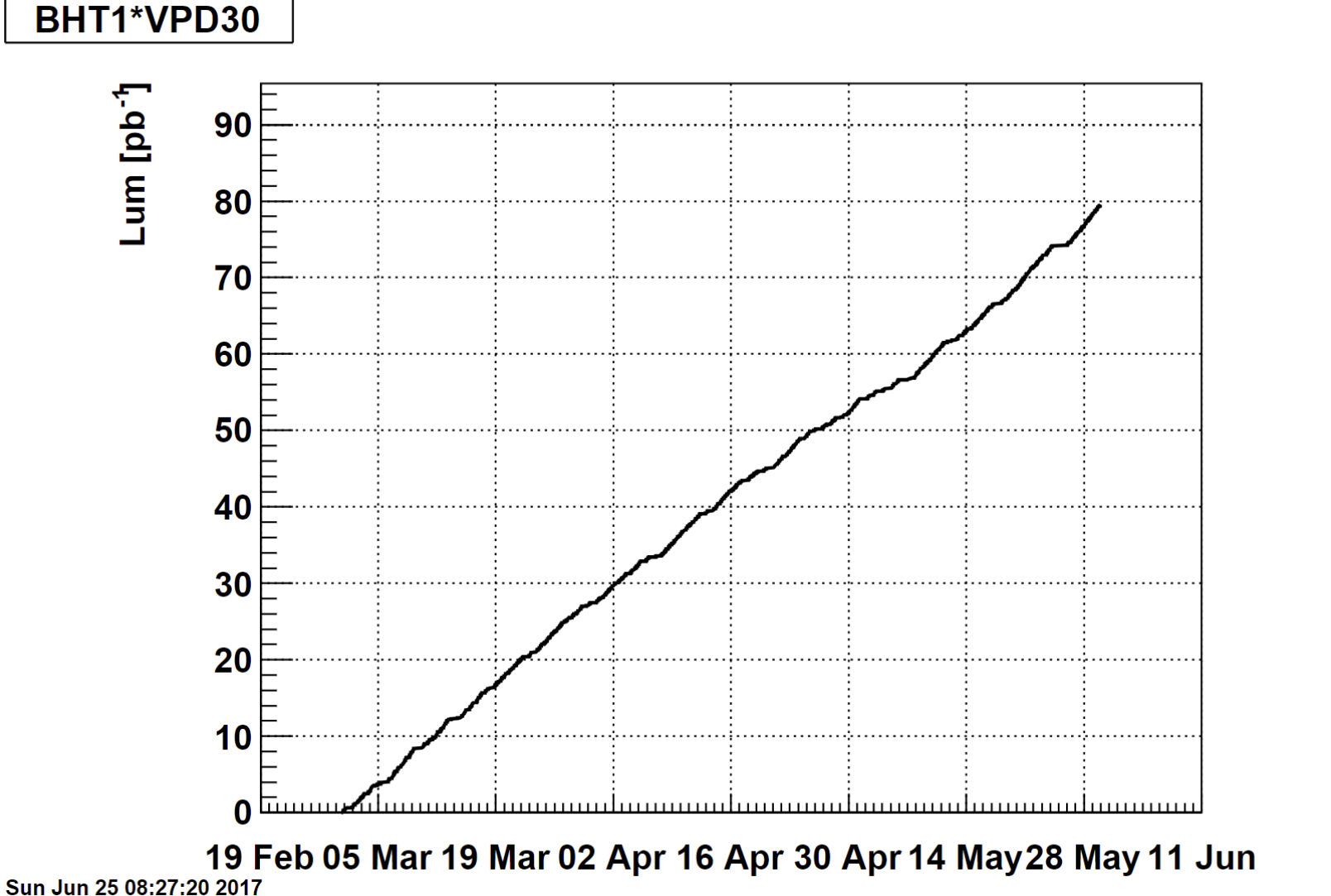
Conclusion
The Path to Data
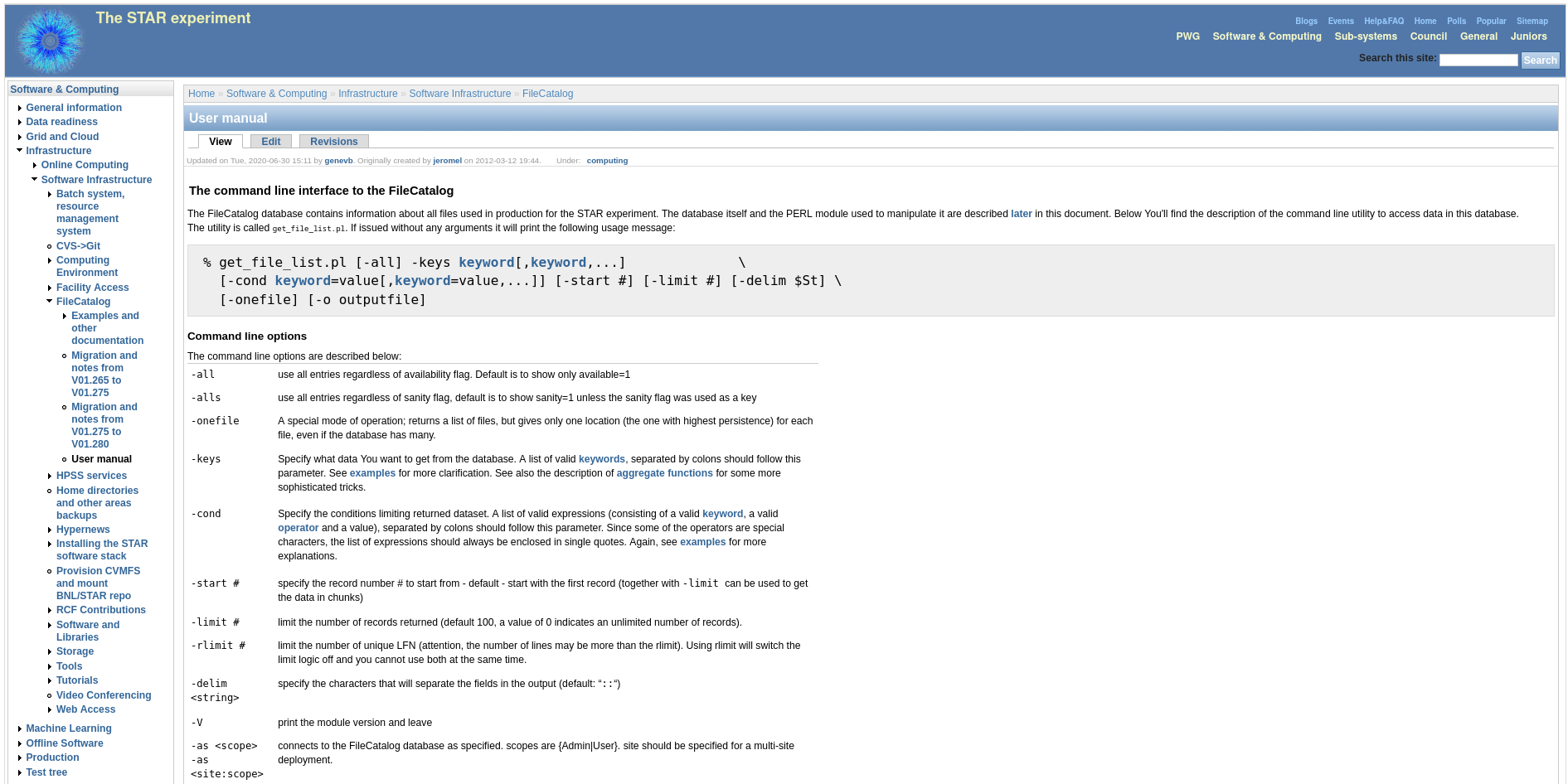
get_file_list.pl - Briefly
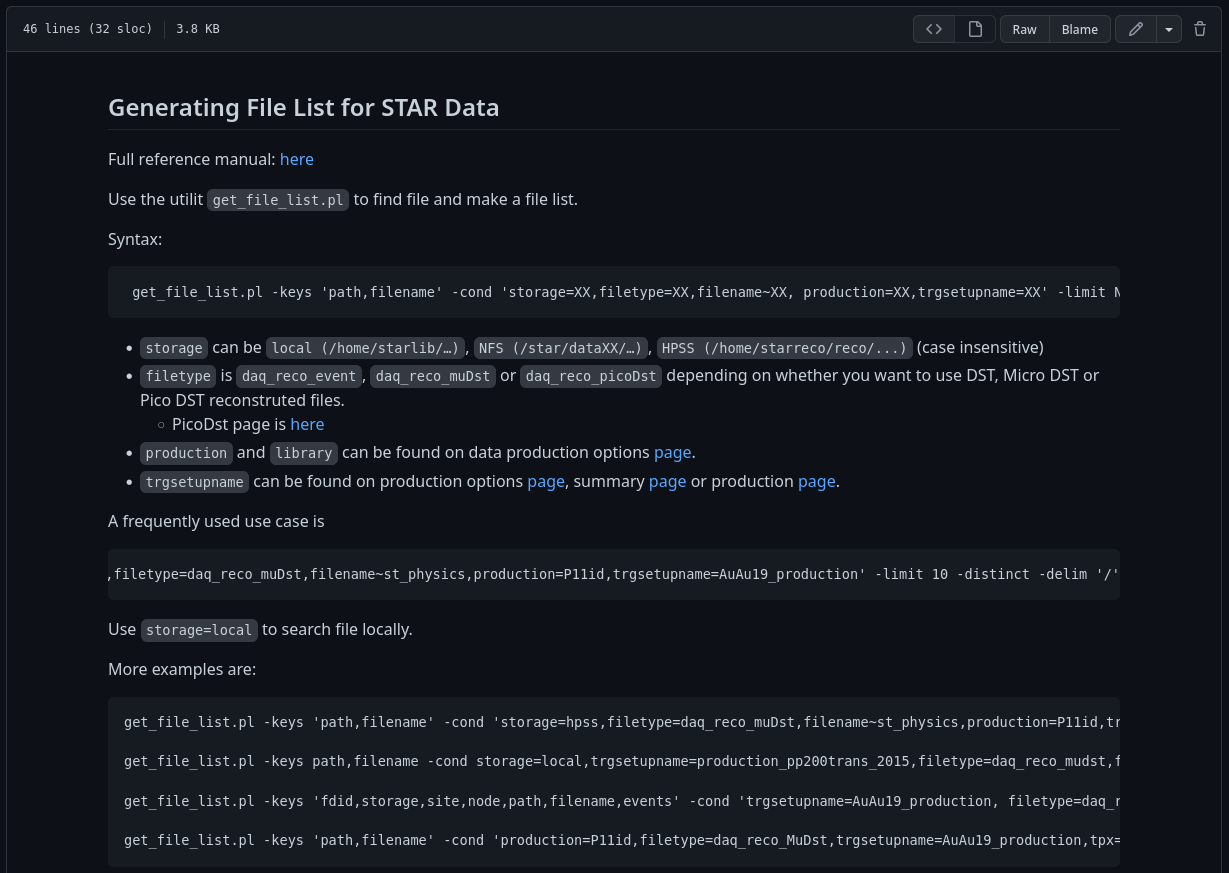
Generating File List for STAR Data
get_file_list.pl - Documentation